Can daily chores be any easier for people? The short answer is “yes, they can”. In fact, they are becoming easier every year.
Smart home technology was first implemented as early as 1975. Since then, it has become a common instrument in millions of houses across the globe. In the US, for example, 48.4% of households will be automated by 2025. How can it change our lives, and what trends should we expect?
Today, we’re going to figure it out.
In this blog post, we are reviewing smart home technology and how it works on mobile devices.
Smart Home: Trends and Statistics
What exactly do we mean by “a smart home”? Under the smart home umbrella, there are interconnected gadgets (IoT) and related services used for home automation.
Here are some stats that demonstrate the industry’s development and what’s waiting ahead (Statista):
- In 2022, the projected market revenue is expected to reach 115,7 billion USD;
- The niche will grow steadily at a 13.3% CAGR from 2022 to 2026. It will result in a market volume of 207,809 billion USD in four years;
- Such market growth causes the expansion of household penetration. In 2022, the smart home’s penetration will be around 14%, and it can reach 25% by the end of 2026;
- On the global level, the US market has the biggest potential for the niche, having a market size of 33,659 million USD.
What’s the secret to smart home’s popularity?
IoT is not just some fancy trend. There are several factors that equally impact the growing popularity of smart household devices. Here are the main ones.

- Rapid technological evolution. Hardware and software potentials are developing every year. Current advancements differ from the ones we’ve known before, which inevitably affects customer expectations and market transformations.
- Emerging cloud computing opportunities. Cloud infrastructure, essential for IoT solutions, is more accessible than ever. Smart home providers can benefit from flexible service options offered by popular cloud platforms, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, etc.
- Obligatory environmental standards. Several developed countries include smart home solutions in their eco-protection measures, for example, the UK (smart meters). It’s become an essential part of the national program.
Types of Smart Home Apps
The market of smart home products is diverse and touches on many aspects of our day-to-day life. These are the main categories:
- Energy management: fans, pumps, dampers, etc.,
- HVAC/R (heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration): boilers, air conditioners of different types, thermostats, etc.,
- Lighting: wireless switches,
- Security: locks, CCTV cameras, doorbells, etc.,
- Household devices and furniture: vacuum cleaners, coffeemakers, clocks, garage appliances, etc.,
- Robots and virtual assistants: Astro by Amazon, Vector 2.0, AIBO by Sony, and others,
- Health and wellbeing: fitness mirrors and trackers, scales, heart rate monitoring devices, connected inhalers, contact lenses, etc.
The best event and conference app: does it exist, and how to build one?
Read more
Most of these devices are connected to mobile apps to make them as handy as possible and provide continuous control and monitoring. Depending on the goals and complexity, IoT apps can manage one or several interconnected devices:
- One app for one device. This is a good option if you produce one product only (for example, a virtual assistant) and are not going to expand the assortment;
- One app for several devices developed by one brand. Building one app for a range of devices improves customer satisfaction and reduces your development/enhancement costs (instead of several apps, you have to optimize one);
- One solution for cross-category devices developed by multiple brands. These are complex platforms to control and automate all devices in the house.
What Are the Key Elements of a Smart Home Solution?
Any smart home system contains three elements for smooth operation: hubs, sensors, and actuators. Let’s examine them in more detail.
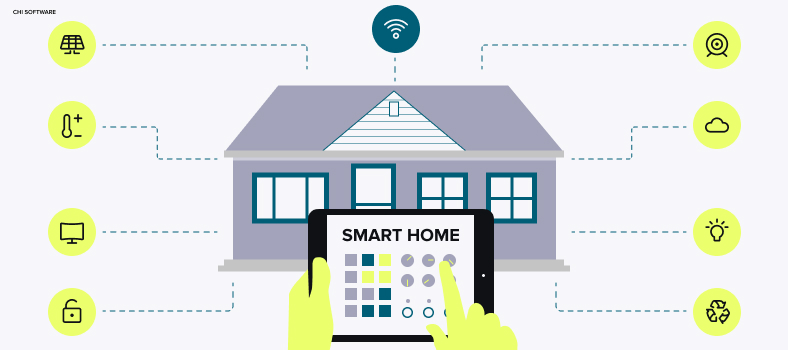
How smart home systems work
1. A hub or mobile app
This is a control center that monitors available smart devices in a house and processes their data. A hub is like the brain of any smart home infrastructure. It has a powerful backend part (server side) to connect all devices and a frontend part (client side) usually in the form of a mobile app.
Through hubs, users manage a smart home ecosystem, either manually, or by setting up automatic responses to various circumstances (for example, adjusting air conditioning in response to the weather outside).
In recent years, mobile apps have been gradually displacing smart home hubs on the market, offering a simple and fuss-free workflow.
2. Sensors
These devices collect information about the environment: temperature, movements, humidity, and others to transfer it directly to the hub. Sensors are like the eyes and ears of an IoT ecosystem.
After receiving data from sensors, hubs react accordingly. They either send notifications to the user or respond automatically to changing conditions.
3. Actuators
This term refers to myriads of IoT devices available on the market, such as smartwatches, TVs, thermostats, refrigerators, etc. Actuators receive commands from the hub and change their status or parameters.
How smart home elements connect with each other
Any IoT infrastructure needs a connectivity method for seamless communication between a hub, sensors, and actuators. There are four connectivity types to choose from:
- Wi-FI is considered to be the most popular communication protocol for IoT devices. At the same time, it requires the most energy, so devices should be regularly charged.
- Bluetooth is less common than Wi-Fi, but at the same time, Bluetooth devices are cheaper and consume less energy. Their biggest disadvantage is low connectivity capabilities. All IoT elements should be located closer to each other, and users can’t control their IoT system outside the house.
- Z-Wave is a low-power mesh network* providing high connectivity, which allows adding any number of devices to the network. At the same time, the Z-Wave signal reaches 100 meters max, so users can’t control their homes from afar.
- Zigbee is another affordable low-power mesh network for connecting smart home devices. Zigbee provides secure data transmission using 128-bit cryptographic keys and controls devices within 10-100m indoors. The Zigbee Alliance now includes more than 600 companies (like Siemens, Philips, Bosch, and others), meaning there are thousands of ZigBee-friendly devices, and their number is growing each year.
* Mesh network is a network of devices (nodes) linked together to share data. Each device can transmit a signal by connecting to the local Internet.
HomeKit: Apple’s Smart Home Platform
HomeKit, first announced within the iOS 8 update in 2014, ties together smart home gadgets and all types of Apple devices (iPhones, iPads, etc.).
Smart home manufacturers have to follow specific requirements to receive HomeKit certification. It was especially challenging back in the day when Apple demanded a hardware security chip in every device. But in 2017, a new software-based solution made things easier and opened doors to more smart home tools in the HomeKit ecosystem.

The idea behind HomeKit is to enable users to control their homes within Apple infrastructure using the pre-installed Home app. Of course, not all devices are now compatible with HomeKit, so one has to download a separate app for such products.
The Home app
Home was released two years after HomeKit, with the iOS 10 update. It allows users to control their homes and keep things in order in different ways: manually, by setting up automatic actions for specific devices, or by creating “scenes” for several devices at once. The scene feature, in particular, is one of the biggest Home’s advantages.
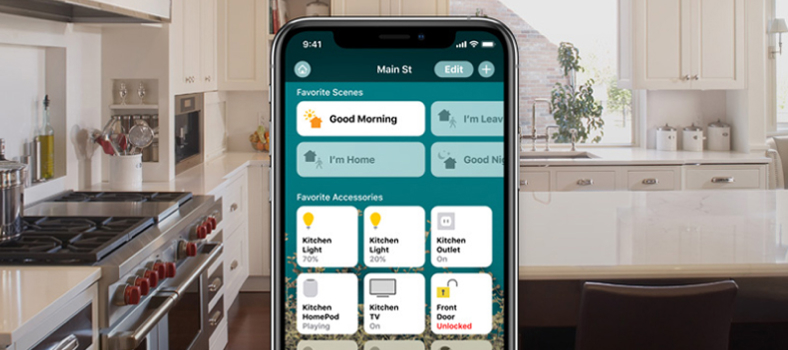
The scene in the Home app
For example, the “Good Night” scene may include locking doors, turning the lights off, or turning night lights on if some motion is detected. All of it happens automatically with no additional human intervention. Similarly, users can create scenes for mornings, for when they get back or leave home, etc.
Also, smart devices can be grouped into “rooms”. Users mark what devices belong to what rooms to manage and monitor locations separately.
Other examples of HomeKit-integrated apps are:
Smart Home Platforms for Android Users
Is there any Home alternative for Android users? Not exactly. But there are similar smart home options, with a hub and without one.
Google Home
Google Home is the first app that comes to mind in the context of Android home automation. It helps users manage devices created by Google (like Nest and Home) as well as numerous accessories produced by other manufacturers.
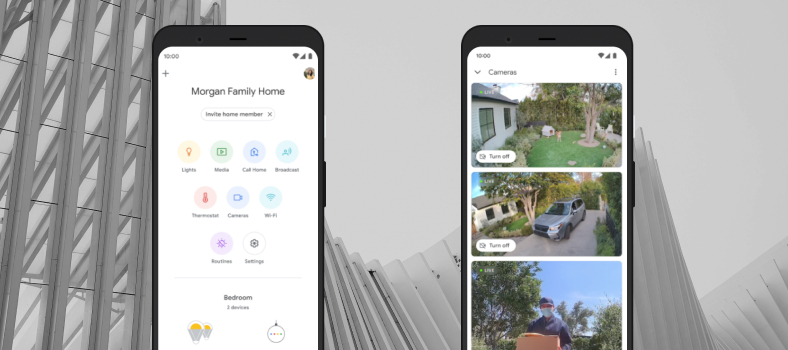
However, not all devices compatible with Assistant are supported by Google Home.
Features:
- One view of a smart home system,
- Easy adjustment of any smart device within the app,
- Routines to integrate repetitive actions,
- Rooms to control all devices located in a particular location.
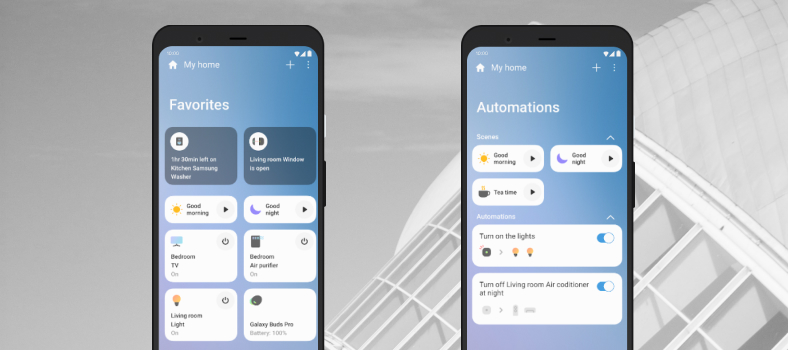
Samsung SmartThings
Even though SmartThings was created by Samsung, the list of supported devices is not limited to this brand only, but still, it is shorter than Google Home’s.
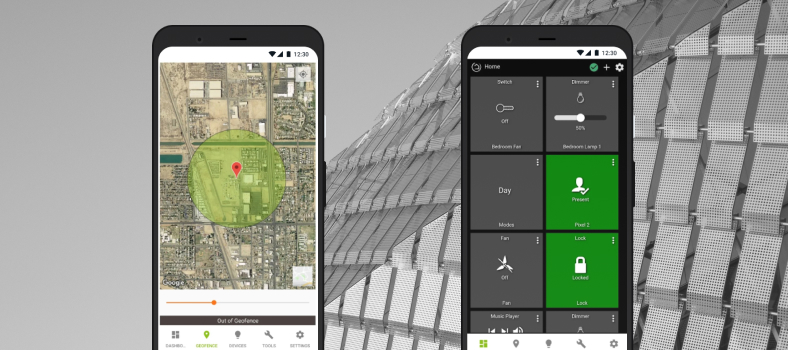
Features:
- Controlling and adjusting each smart device separately,
- Automating typical smart home tasks (for example, turning off the light at a given time),
- Scenes to automate groups of devices,
- Favorites to quickly access the most frequently used devices and scenes.
Alexa Smart Home
Alexa Smart Home is an impressive ecosystem powered by Amazon with the Echo device and Alexa assistant at its heart. Echo is a smart speaker processing voice commands with Alexa’s help. Applying Echo is optional, as customers can use only a mobile app to manage their homes.
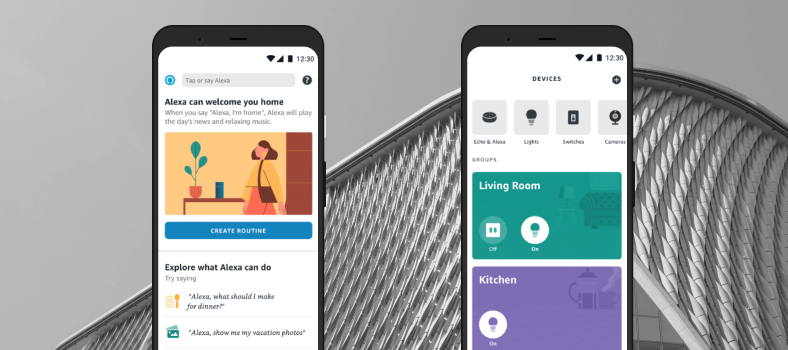
Features:
- Routines for repetitive actions,
- Guard which sends alarm notifications from the Echo device,
- Hunches enable Alexa to suggest or remind users to do something (for example, close a door when a user is away),
- Printing documents through voice commands.
Hubitat Mobile
This app is an addition to the more complex Hubitat Elevation Platform providing smart home hubs. It is for those seeking advanced features and security.
Features:
- Advanced Dashboards to manage devices,
- Device organization by Rooms,
- Geofencing to send alerts to the system if a user is close to the house (or not at home) after entering (or exiting) a defined “fence”,
- Secure access to the system, even with no available Internet connection.
What Are the Key Advantages of Smart Home Hubs?
Why would users choose smart home hubs over more simplified mobile solutions? The answer is hidden in these advantages.
1. Additional security layer
Hubs serve as connectors for all smart home devices and, at the same time, provide advanced security, which is especially beneficial for office spaces. Modern hubs are usually equipped with two-factor authentication to limit access to the system.
2. Support of several connectivity methods
Smart home hubs, unlike mobile apps, support all connectivity methods, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave.
3. Broader range of connected devices
Users can create more sophisticated scenes and routines if they connect every gadget to one system. Supporting all communication protocols, hubs are essential tools for building complex smart home ecosystems with accessories from multiple vendors.
Our Experience in Building a Hub-Based Smart Home System
Our team has extensive expertise in building IoT solutions for various business domains. One of them is smart home technologies. Here is our story and project description.
Client introduction
Our client is a US technological company formed back in the 1970s with a goal to simplify people’s common activities at home and at work. The company’s product assortment has changed and grown through the years. Now, our client offers software and hardware for numerous corporate clients (enterprises, campuses, hotels, etc.) as well as individual households.
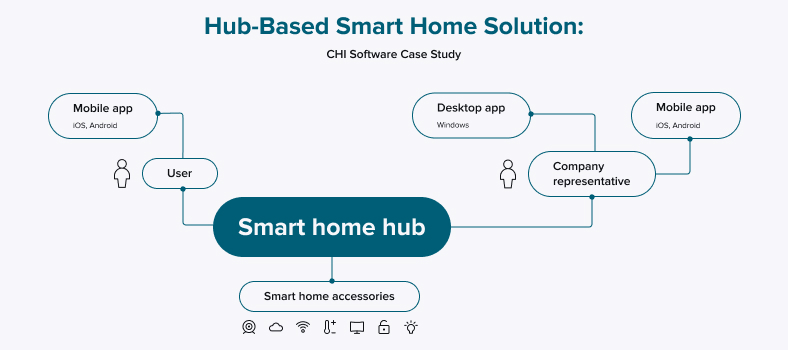
The project’s main idea and structure
The product we are currently working on is a sophisticated hub-based smart home solution with advanced security. A user can manage and monitor smart home accessories by connecting to a hub. This hub, in turn, is connected to a mobile app via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.

Software and hardware involved in the project:
- A smart home hub. This is a hardware device with microcontrollers;
- A supporting desktop app to enhance and update the hub (Windows OS). It is a solution with advanced settings used by company representatives. To communicate with the hub, representatives connected it with their laptops through an Ethernet cable;
- A supporting mobile app to enhance and update the hub (iOS, Android). Later on, emerging mobile technologies allowed improving the workflow. The company considered creating a mobile app for the tasks accomplished by the desktop app.
Initially, such an app was built using cross-platform tools (JavaScript and Apache Cordova), but this approach has several drawbacks. One of them is that only native solutions support Bluetooth connection, which is the optimal way to communicate with the hub. So the decision was made to build two native apps;
- A user app (iOS, Android). This is a solution for final users with an intuitive interface to quickly organize and automate daily smart home activities.
There are several dedicated teams working on the two types of mobile apps. CHI Software is taking part in building the supporting iOS app for the company’s representative. Our client’s partnering company is responsible for building and enhancing the project’s hardware.
The solution’s flow
- The user buys a smart home device (hub) from our client.
- Before setting up a hub, the user should sign up in our client’s system. It provides enhanced smart home security.
- Then, the company’s representative helps set up a hub at a user’s place using a special mobile app.
- To control the system remotely, the user downloads a mobile app and connects with the hub via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
What now?
The solution is already being offered to individual customers in several countries. At the same time, the project is not over and has a lot of potential and work to be done in the near future:
- Expanding the list of supported smart home accessories,
- Finishing up the supporting mobile app by adding all features available on the desktop app;
- Enhancing the solution’s security for corporate clients.
Conclusion
Modern homes are smart enough to help you manage your daily routine and monitor the household’s safety with your smartphone. How far will innovations lead us? Soon, we will figure it out. This is what we know so far:
- The smart home niche is expected to grow steadily at a 13.3% CAGR from 2022 to 2026;
- There are three main contributors to the niche’s growth: technological innovations, emerging cloud computing capabilities, and updated environmental standards;
- Among the key smart home product categories are energy management, HVAC/R, lighting, security, household devices & furniture, robots & virtual assistants, and health & wellbeing;
- Any smart home system consists of sensors, actuators, and a hub (or a mobile app);
- Users can manage their smart homes with their Android or iOS device. Apple users can use a default app called Home to manage HomeKit-supported devices;
- Special hubs are a good option for rich smart home ecosystems requiring several connectivity methods.
About the author
Polina is a curious writer who strongly believes in the power of quality content. She loves telling stories about trending innovations and making them understandable for the reader. Her favorite subjects include AI, AR, VR, IoT, design, and management.
Rate this article
22 ratings, average: 4.5 out of 5












