In recent years, practically every industry has experienced some form of digitalization. This comes as a natural response to the growth of the digital sphere. Digitalization has made users accustomed to the convenience of getting services and products quickly and without leaving the comfort of their homes.
The healthcare industry is no different. It was one of the first industries to embrace it, and nowadays, it feels the full extent of the main challenge that comes with this process. What is that challenge, you might ask? Security.
The Importance of Healthcare Data Security
Recently, CHI Software did a survey among healthcare and wellness businesses. One of the questions we asked was: what is the biggest challenge currently hindering the growth of the health tech and wellness industries?
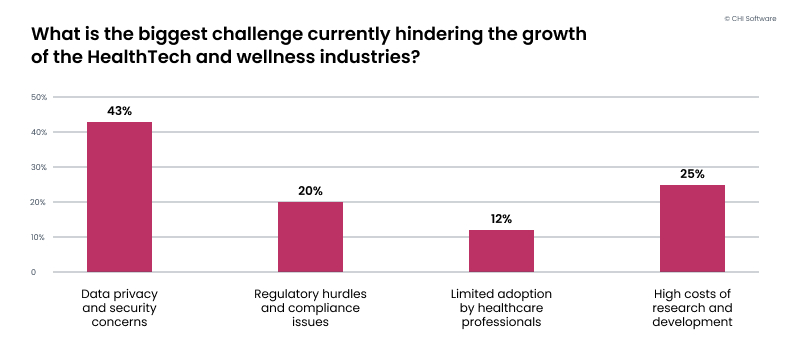
As you can see, almost 45% of the respondents pointed to data privacy and security concerns. This correlates with the answers we got for another question: which skills do you believe are currently in the highest demand but in low supply?
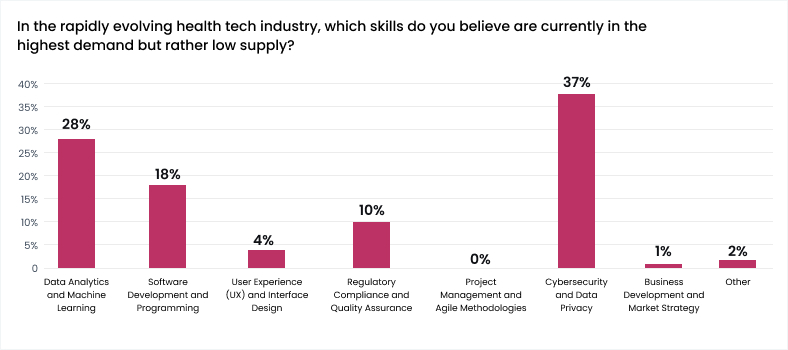
Again, more than 35% of business owners felt the lack of cybersecurity and data privacy specialists. But why are so many healthcare and wellness industry representatives concerned about security?
The answer to this question comes from the statistics. Healthcare organizations all around the world were targeted by malicious actors on average 1,463 times per week in 2022. That’s roughly eight attacks every hour! If they were to access a patient’s data, the consequences could range from inconvenience to catastrophe.
- From the patient’s perspective, their data could be used to receive treatment or file false medical claims. Even more concerning is that data has a long lifespan and could be valuable to hackers for years to come.
- From the business perspective, a data breach is an unpleasant surprise that can seriously impact operations. A minor scenario could involve temporarily losing access to your database due to installed ransomware. . In the worst case scenario, you could potentially lose all your data, bringing your entire business to a screeching halt.
That’s why security has become a major main concern in the healthcare and wellness industry. But what are those threats? Let’s talk about them.
What are the Most Common Medical Cybersecurity Threats?
Cyberattacks are divided into different categories based on the type of malicious software (malware) they use. The most common attacks the healthcare industry suffers are:
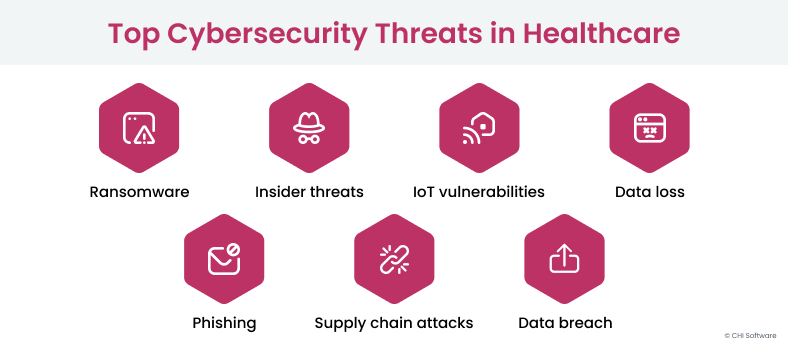
Ransomware
This type of malware holds the victim’s device or data hostage until they comply with the hacker’s demands – usually to pay up to call off the attack. According to the IBM report, such attacks represent 17% of all cyberattacks in 2022.
There are two types of ransomware:
- Encrypting ransomware is the most common one. It encrypts the victim’s data and then asks for a ransom payment in exchange for decryption.
- Non-encrypting ransomware is less common. It blocks the victim’s entire device by locking access to the operating system. When booting up the computer, the victim will see a screen asking for ransom instead of their desktop.
In recent years, ransomware attacks on hospitals have become even more malicious: they ask for ransom multiple times after the first one is paid.
Phishing
Phishing is a scam that attempts to trick users into exposing sensitive data through fraudulent emails, text messages, phone calls, or websites. Phishing attacks in healthcare are the most common type of cyberattack.
This method is considered cheap compared to others since it relies simply on tricking people instead of hacking them. It’s based on social engineering, deceiving, pressuring, and manipulating people into sending data to malicious actors.
The attacker usually masks themselves as someone the victim will trust – their coworker, boss, or the company the victim works with. Then, the attacker creates a sense of urgency to make the victim act without thinking carefully.
Everything you need to know about mHealth app development
Read more
Insider Threats
All the attacks we’ve talked about until now were outsider attacks. Insider attacks, however, originate from authorized users. Intentionally or not, these users share their data access or have their accounts hijacked by malicious actors.
There are three types of insider threats:
- Malicious insiders: These users are usually current or former employees whose access hasn’t been revoked;
- Negligent insiders: They don’t have any malicious intent but create security threats through negligence;
- Compromised insiders: This is a legitimate user whose credentials have been stolen.
While external attacks are still more common, insider threats can be more dangerous and costly for businesses. Such attacks cost US companies around $4.9 million USD in 2023.
Data Breach
This type of attack covers all security incidents where unauthorized users gain access to sensitive information. This term is often interchangeable with cyberattacks. However, there are differences:
- Data breaches include only those security breaches where data is compromised;
- Cyberattacks include every security threat with malicious intent.
Data breaches take a lot of preparation time and are hard to execute.
IoT Vulnerabilities

Despite wearable technology being a blessing for the healthcare and wellness industry, it can also be vulnerable to security issues. Here’s a couple of examples where such tech is lacking:
- Weak or hardcoded passwords. IoT devices can be vulnerable targets for malicious attacks because default passwords for the onboard hardware used for most wearable tech can often be programmed in the factory with something basic as “1111” or “admin”;
- Insecure network services. Most IoT devices are vulnerable to “Man-in-the-middle” (MITM) attacks. Such attacks are intended to capture data during the transfer and then use it for malicious purposes;
- Lack of secure update mechanisms. This is the most common attack on IoT in healthcare. Unauthorized software and firmware updates are devastating since wearable technology usually doesn’t have methods to verify where the update came from;
- Insufficient privacy protection. The main purpose of wearable technology is to collect patient’s data and transfer it to doctors. However, without proper access control, it can expose a patient’s sensitive data to malicious actors;
- Insecure data transfer. The data collected from patients is stored and transferred to other devices automatically. Sometimes, these minimal programs don’t include checks to verify where exactly this data is sent to. This means that hackers don’t need to intercept data, they can just transfer it directly to themselves without anyone noticing it.
Learn more about IoT use cases in healthcare from our guide
Click to read
The listed vulnerabilities come down to the nature of IoT. A device that operates on low power with limited functionality doesn’t leave much room for proper protection protocols.
That said, it’s not all gloom and doom for IoT. If you have a team of expert developers by your side, you can easily mitigate all of the shortcomings of IoT. For example, here at CHI Software, we are experts in IoT technologies and data protection.
Supply Chain Attacks
Sometimes, hackers don’t target businesses directly. And why would they? It is easier to target a vulnerable third-party business instead of a head-on attack on the primary target, which is likely to have tighter security.
That’s why supply chain attacks are also known as third-party attacks. This type of attack is when a hacker infiltrates a business’ system through a third party.
Developing Wellness Apps for Seniors: Accessibility and Usability Considerations
Read more
Such attacks have been on the rise recently due to enterprise companies shoring up their security. Supply chain attacks come in different varieties:
- Upstream server attacks are the most common type. Hackers infect a server with malicious updates, which are then automatically distributed among users;
- Midstream attacks target means of production such as software development tools;
- Dependency confusion attacks exploit weaknesses in the internal software by registering an infected system build as the new update that is distributed to the company’s computers;
- A stolen SSL attack compromises private authentication keys for websites or cloud services;
- Open-source software attacks exploit the ability to introduce new builds for open-source systems and distribute new versions to all users.
You shouldn't worry about cybersecurity threats if you hire the right talent
Hire us!
Data Loss
Data loss is the intentional or accidental destruction of data, which can be caused by people or processes within or outside of the organization.
Data loss is similar to a data breach. A data breach doesn’t always end up destroying the original data. There are many reasons why it can happen, and not all of them imply malicious intent. Let’s look at how data loss can occur:
- Hardware malfunction is the most common cause of data loss. Hardware can crash due to a variety of reasons, which can be summarized as improper maintenance;
- Software corruption can result from mishandling software or critical bugs in software;
- Natural disasters can sometimes cause data loss when the data servers are physically damaged. It’s hard to classify natural disasters as malicious or negligent; however, they still cause security threats;
- Malware. As we already explained, some data breaches can lead to data loss.
Now that we have covered the main methods of attack, you might be wondering: how do I protect my business? Let’s open our portfolio and look at the case study.
How to Protect Patient Privacy and Security: Our Experience
In June 2020, a client contacted CHI Software with an idea to create a healthcare platform with diverse functionality for patients and doctors. After discussing the details of this project, we decided to start development in the healthcare marketplace.
AI-Powered Training App Development: The Ultimate Guide
Read more
Next, we added a set of features:
- Online consultations so that patients can contact doctors via video calls or chat;
- Appointment reminders to help patients and doctors remember about their plans;
- A scheduling system for doctors so they could properly plan their work;
- E-prescriptions created by doctors with no need for paperwork;
- A payment system allows patients to buy their medications according to e-prescriptions from their doctors.
This platform had to support high loads of data because it would have many end-users. Since the project involved sensitive patient data, we had to create a proper security system. Here are our insights.
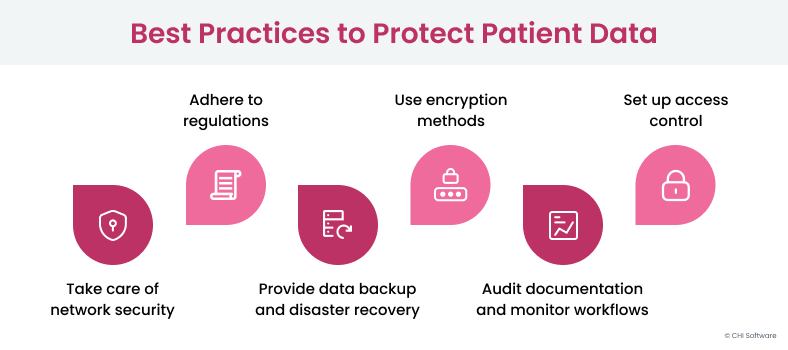
Compliance
Our healthcare solution is designed to adhere to local laws and regulations, ensuring full compliance and utmost protection of user data.
These laws and regulations on medical data protection vary depending on the country you expect to work in. For example, if you are developing eHealth software for the US, HIPAA compliance and cybersecurity should be canon for your business. The same solution for the EU will require GDPR compliance.
Th 15 Examples of How to Use Machine Learning in Healthcare?
Read more
Encryption
In our case, all sensitive data, such as patient records and financial data, is encrypted both in transit and in storage. Encryption helps to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that data remains confidential.
There are numerous encryption algorithms available, but they are generally divided into two types:
- Asymmetric encryption method. This method encrypts data with two separate cryptographic asymmetric keys. The most common method is called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which governs encryption through the management of digital certificates. These certificates determine which users can access the information.
- Symmetric encryption method. Contrary to the asymmetric encryption, this approach uses only one secret key. The most common method is called Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) – currently the gold standard for data encryption worldwide.
Data encryption in healthcare is very beneficial, as it provides a way to manage user information access based on their security clearance level.
Access Control
Our solution uses the most popular and reliable data protection methods. Let’s look at them:
- Authentication and authorization. Put simply, authentication is the process of verifying users, while authorization is the process of verifying what data those users have access to. Some healthcare organizations have already introduced biometric security in healthcare.
- Password policies. The more simple a password is, the faster hackers can guess it. That’s why there are rules for creating strong passwords: for example, using at least eight characters with different types of symbols (letters, numbers, and special characters).
- Role-based access refers to the idea of assigning permissions to users based on their role in the organization. This way, someone who has low-security clearance won’t access sensitive data and will only see the data they need for work.
These practices are not exclusive and work best when combined together. Access control lowers the risk of insider threats and data breaches.
Network Security
Protecting your data is just one part of cybersecurity. The data is still vulnerable while it’s being transferred.
Healthcare network security works at two levels: inside of the network and on its perimeter. At the perimeter, security tries to stop any ongoing cyberattacks. Security inside the network is a safety measure in case the network’s perimeter is breached.
To create a healthcare data breach prevention system for our solution, we combined these tools:
- Firewalls are software that stops suspicious traffic from entering or leaving a network. They are used to divide organizations’ networks from the outside world or inside the network to divide it into subnetworks;
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPSs) do exactly what their name implies – they detect and prevent security breaches;
- Prevention systems are tools that continuously monitor networks for malicious activity and take action to prevent them;
- Regular vulnerability assessments include scanning, detecting, and analyzing security vulnerabilities within a corporate network infrastructure.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
This process involves periodically creating and updating file copies, storing them in remote locations, and using them to resume operations in the event of data loss.
Some people mistakenly use both terms interchangeably. Still, there is a difference:
- Backup is the process of making file copies;
- Disaster recovery is the plan for using the copies to reestablish access to data and other resources quickly.
This method doesn’t deal with cyberattacks directly. It creates a means to recover operations after the cyberattack happened. There are a couple of ways to backup and recover data:
- Cloud-based backup solutions have recently become more popular. They are cheaper compared to other methods since they don’t require your business to have physical infrastructure to store backup files. On top of that, they provide the necessary distance and scalability to keep data safe;
- On-premises backup refers to having physical infrastructure for backups in the business. This is the most popular way to store backups for the healthcare industry since many legal regulations require physical backups to be accessible;
- Snapshot-based replication creates and stores the system’s current state. Each time a new snapshot is taken, it rewrites only changed data parts. This method is very effective as you can rollback your system to the latest snapshot and, in the worst case scenario, you will lose only a couple of hours of data since the latest snapshot;
- Continuous replication is the most efficient way of backing up your data as of today. With this method of healthcare data backup and recovery, the system’s latest copy is continuously replicated to another location or in the cloud, thus minimizing downtime.
Auditing and Monitoring
Auditing is the process of reviewing documentation in retrospect to determine if the business has followed procedures and performed services correctly.
Monitoring is a means of setting up a mechanism to prevent transmitting inaccurate information to end users.
This step also helps evaluate the businesses’ compliance program and make internal controls more effective.
Now, you know all the best practices for patient privacy and security. Remember that these best practices are most efficient when combined.
But what does the future hold for cybersecurity in healthcare? Let’s talk about what to expect next.
The Future of Healthcare Information Technology Security: What Will Change?

The future of cybersecurity in healthcare looks bright! Potential threats are always emerging, but so are the methods of preventing them. Here’s what to expect.
Increased use of AI and machine learning. Artificial intelligence can detect and prevent cyberattacks faster compared to human peers and other software. The only thing algorithms need is training data to learn from. If you’re interested in this technology, we at CHI Software can provide healthcare AI consulting for you today.
Predictive analytics in healthcre: what it is, and how to implement it for your advantage
Read more
Focus on a Zero Trust Policy. This approach is based on implying that every entity (internal and external) shouldn’t be trusted by default. Nowadays, this approach is already utilized by some healthcare organizations. However, in the future we can expect to see this approach to be more widespread.
Blockchain and data security. This method is based on cryptography, decentralization, and ensuring trust in transactions. Since the vulnerability of any type of information is its centralization, blockchain security can mitigate this problem.
IoT security. As of today, one of the biggest flaws in wearable technology is the lack of security. We can expect this issue to be resolved in the future with the introduction of new healthcare cybersecurity solutions.
Cloud security. Cloud-based solutions have risen in popularity across healthcare. This means that quite soon, cloud security in healthcare will improve in order to comply with regulations and laws.
Final Thoughts
The importance of cybersecurity in healthcare cannot be overstated. The sensitive nature of patient data makes it a priority target for hackers. With a great variety of attacks being faced, healthcare organizations should abide by patient data security standards.
Sadly, there is no such thing as impenetrable protection. Still, your business must be ready for the most common attacks.
We at CHI Software have experience developing healthcare solutions and know how to make them secure. Additionally, we are experts in AI and can utilize it to protect your data. Intrigued? Don’t wait another minute to contact us and discuss your business idea.
FAQs
-
What is cybersecurity in healthcare?

Cybersecurity refers to practices and measures for protecting sensitive patient information involving encryption, access control, authentication, and regulatory compliance.
-
What are the most common cyber threats for healthcare organizations?

The most common medical cybersecurity threats include ransomware, phishing attacks, insider threats, data breaches, IoT vulnerabilities, supply chain attacks, and data loss.
-
How can healthcare organizations protect patient data?

Electronic health records security is a top priority for healthcare organizations. To secure data, organizations should utilize encryption, access control, backups, and network security. On top of that, they need to ensure regulatory compliance and conduct regular auditing and monitoring.
-
What are the consequences of a healthcare data breach?

Data breaches can lead to a variety of problems: identity theft, legal and regulatory penalties, and financial loss. This can lead to a damaged reputation and loss of competitive advantage.
-
How does telemedicine impact healthcare cybersecurity?

Telemedicine presents challenges to healthcare cybersecurity since it expands the digital interface between patients and doctors. This leads to a higher risk of data breaches and cyberattacks. To combat these challenges, healthcare providers need to ensure robust encryption protocols of data transfer, as well as compliance with healthcare regulations. On top of that, since most patients and doctors use their personal devices for appointments, network security is a necessity.
About the author
Ivan keeps a close eye on all engineering projects at CHI Software, making sure everything runs smoothly. The team performs at their best and always meets their deadlines under his watchful leadership. He creates a workplace where excellence and innovation thrive.
Rate this article
22 ratings, average: 4.5 out of 5








