Private health insurance companies have worked on the global market for a long time, and the industry is enormous. But, not many businesses in the healthcare sector consider the need for mobile health insurance software and neglect it. By doing so, insurance companies lose a significant part of their customers. According to the Accenture 2020 Digital Health Consumer Survey, 75 percent of patients understand the importance of healthcare apps and are ready to use minimal personal insurance programs.
Mobile healthcare insurance software can help companies offer users a better service, improve decision-making, and provide precise information in real time. They are convenient, fast, easy for customers and increase income for businesses. These benefits are achievable if you understand what the solution should be and what you expect from it.
This article will discuss health insurance software‘s advantages, business models, and features.
Insurance and Healthcare Mobile Apps: Market Size and Trends
Healthcare and insurance apps are gaining traction these days! According to the statistics, the insurance business market was valued 81.7 billion USD in 2023 and is projected to nearly double 156 billion by 2028.
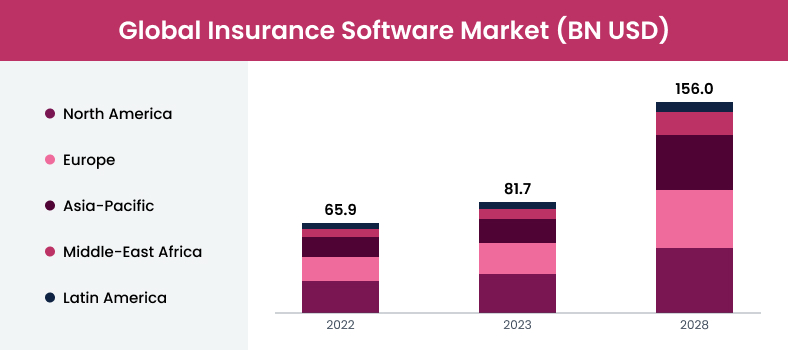
Meanwhile, the mHealth (Mobile Health) market, which was worth 34.8 billion USD in 2018, is expected to skyrocket to 832.88 billion USD by 2032. So, what’s driving their popularity?
The main reason is that companies want to improve the customer experience. With almost everyone owning a smartphone today, it’s much easier and more convenient to access all kinds of services. Plus, managing services through apps means companies need fewer employees, but can still provide great value to their users.
A great example is the Aetna life insurance company. They offer life insurance services through mobile apps and have around 39 million customers in the US alone, making them one of the biggest insurance providers. But what exactly makes these apps so profitable? Let’s look at their benefits and features.
Benefits of Health Insurance Apps
The proliferation of mobile health (mHealth) and online health insurance software is driven by multiple benefits for both patients and providers. Healthcare applications combine the functional environment and solutions to manage company workflows and improve information exchange between clients and personnel.

Mobile technology turns healthcare insurance apps into useful customer service tools that eliminate the need for intermediate agents.
For Customers:
- Easy doctor search in the insurance network and on-demand access to all specialists;
- Authorized and secured permission to message the doctor;
- No need to visit the clinic and feel unnecessary stress due to asking small questions;
- Lower cost of service and higher ease of use with apps accessible on any device;
- Getting the insurance and coverage without excess paperwork;
- A private treatment plan that meets the customer’s needs.
Telehealth App Development: Everything You Need to Know
Read more
For Business:
- Enlarging the base of clients due to access to home care and discharged patients;
- Better customer service by eliminating long queues, cancellations, missed appointments, and long claims processing;
- Increased efficiency in both onsite and remote workplaces and freedom to collaborate with various specialists on patient cases;
- Personnel optimization: fewer dedicated call center employees are required, and each manager can work with a large number of clients;
- Quick integration with electronic health records (EHR) and other clinical systems and easy data exchange between clients and the insurance company;
- Ability to treat more patients simultaneously, attract new customers, scale the business, and increase revenue.
What to Expect: Features of Health Insurance Apps
We must list the main features required to figure out how to build a health insurance app.
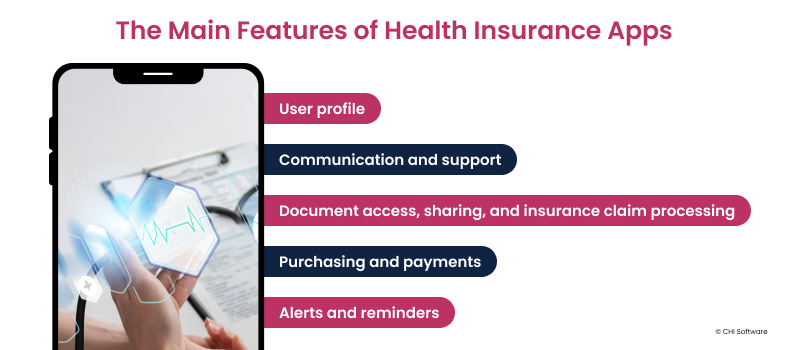
User Profile
This feature is necessary for doctors to continuously compare test results and monitor each patient’s health. Like hospital cards, profiles accumulate crucial medical data stored in a cloud (recommended).
To make it even more useful, allow users to choose a health insurance company plan using a questionnaire or provide information about available options. Comparison tables or charts make comparing characteristics, features, prices, and managing programs easy.
Communication and Support
There are three essential types of doctor-patient communication: voice calls, video streaming, and chat messaging. The first one is a must-have feature that allows customers to urgently call a doctor or nurse and get answers to basic health questions.
You also have to add video for a one-on-one chat with a doctor while developing health insurance software. In recent years, the quality of smartphone cameras has increased significantly, and specialists can conduct fairly accurate examinations remotely, noticing even small visual disease signs. To set up streaming, you need integration with an API like Twilio.
Live text chat with doctors is useful for patients and allows managers to answer clients’ questions and work with several users simultaneously. It is crucial to ensure the chat privacy and provide additional options like uploading documents directly to a dialog. Chat must be encrypted with end-to-end encryption SDK.
Support should be available to users around the clock. To take the extra burden off specialists, install a health questionnaire in the insurance app and provide a FAQ section.
Document Access, Sharing, and Insurance Claim Processing
This feature saves time filling in long forms or sending emails, making it easy to find health insurance documents and send them to managers. To ensure safety when sharing medical records, we have to use encryption.
The app should allow the lab results, prescriptions, and medical records to be kept in one place. If the solution enables physician–patient communication, users have to be able to share their health documents with doctors.
A mobile app can also sync all data to allow users to see the claim statuses in real-time or even file a health insurance claim by medical bill photo. This option improves customer experience and simplifies the work of company managers.
Purchasing and Payments
If you want to monetize the product, adding a feature that allows users to purchase insurance policies and drugs from the app directly is recommended. In doing so, you must ensure data security and fraud protection. The most suitable tool for card payment integration into web and mobile apps is a gateway such as PayPal, Stripe, Braintree, Dwolla, etc. The technology is also used to handle online money transactions.
A payment gateway safely collects customer data on the app’s frontend part, processes it through payment APIs, and sends it to an acquiring bank or processor for the transaction. The gateway should support authentication with token-storing configuration settings for the Client SDK for better security. For instance, Braintree prefers this method and generates a token using the Braintree Server SDK.
As an anti-fraud measure, you can add CVV validation with options like “CVV doesn’t match,” “CVV isn’t verified,” and “the issuer doesn’t participate in verification.”
Alerts and Reminders
Reminders help doctors and nurses see new patients. Moreover, they help users take medications on time and help them avoid missing an appointment or insurance payment deadline. Push notifications and alerts allow users to immediately learn about the results of the claims processing and other important points.
We at CHI Software go further with our development process and create solutions that help to maintain vital signs, such as insulin levels of older people with diabetes. See how it works in our case study:
Our development team created the Insulin Pump App — a system for effective and accurate insulin delivery. The app also reminds users to take their medication. We provided:
- The schedule of taking/delivering insulin and push notifications that increase the safety level for people with diabetes;
- A simple interface, accurate pulse technology for insulin delivery, and a replaceable reservoir;
- The history of insulin usage recording is stored in a mobile app for further analysis.
The system is compact and convenient, especially for older people. Our app helps users to avoid life-threatening situations and maintain a high quality of life.
Technologies: C, BLE, ARM processors, etc.
Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: Improving the Future with AI
Read more
Health Insurance App Development: Our Experience
In today’s world, many companies in the health insurance industry still handle medical cases manually. This process is time-consuming and cumbersome, with a lot of paperwork shuffling between clients, an insurance company, and healthcare providers. There’s also the risk of human error with so much manual work involved.
One of our clients saw a big opportunity here. Since almost everyone uses smartphones for various services, why not make insurance just as accessible? They approached us at CHI Software, knowing our strong reputation in healthcare app development, to create a mobile insurance app.

Their goals were clear:
- Streamline the medical insurance process with fewer manual steps;
- Make it easier for users to get medical advice and schedule appointments;
- Speed up how quickly requests are processed;
- Develop a mobile app for both IOS and Android, along with a web version for browsers.
To bring our client’s vision to life, we assembled a team that not only launched the initial app but continues to support and enhance it with new features. Speaking of features, we’ve created quite a few:
- User-friendly accounts: Besides the standard registration and login, users can also create their accounts through assistance companies. Each user has a detailed profile with all their important information;
- Convenient medical access: Users can book online appointments with doctors and get remote consultations via text or video. The app comes with multi-language support, making it accessible and helpful for a broader audience;
- Smart scheduling and notifications: We implemented a powerful scheduling system that simplifies planning for both patients and doctors. This works seamlessly with our notification feature, which reminds users of upcoming appointments and lets them view their past interactions;
- Clear insurance coverage: To give users a clear understanding of their insurance, they can download the insurance agreement directly to their phone from the app.
Even though the development process is still ongoing, the app has already brought significant benefits to our client. For example, they’ve seen a 20% increase in new customers thanks to the app.
To dive deeper into this project, read our extensive case study.
Business Models for Health Insurance Software
According to the statistics, the compound annual growth rate of the mHealth market is 14.7 percent. For businesses just entering the market, it means they can make a profit from insurance software development. However, the success of your insurance app is determined by the correct business model. Let’s take a look at some of them.

The “Freemium” Model
This is the standard model employed by most online games. In the case of insurance apps, it’s effective for younger healthcare users and new families. The company creates health insurance software and tests it for free, promoting the viral buzz.
The user base grows, and the owner refines the app and offers paid enhancements or upgrades. For instance, Berlin-based healthcare startup Asana Rebel, which uses this model, has already collected over 150,000 paying subscribers and raised 23.9 million USD in funding. The company’s annual revenue is 2 million USD.
This approach is most justified if the target market is a consumer (a patient). The user accepts the conditions, and advertisers (e.g., Big Pharma) want to pay to appear on the site and sell goods via the app. Another revenue source is payments from physicians who offer their services to application users.
The in-app ad model fits well with free healthcare products and is used by 10 percent of owners, according to a Research2Guidance report. Selling prescription drugs in the app is also profitable. For example, the CVS/pharmacy app, which operates on this model, generates about 5,000 USD monthly in revenue and has been downloaded 300,000 times by October 2020.
Big Data, Big Impact: How Analytics Are Transforming Healthcare
Read more
The Licensure Model
Some apps are monetizing through licensing agreements. They assume that the IT companies transfer the software’s rights after the development process for a period in exchange for a fee. This business model fits companies with an existing user base and more than 1 million USD in revenues, and hospitals are revamping their medical systems.
Apps that use licensing to generate income are downloaded approximately 415,000 times yearly. For their owners, the revenue sources are:
- Licensing a dashboard, service, or device to clients;
- Adding development fees, service sales, and sponsorship fees; and
- Selling medication and other products through an app.
A fascinating income source is the sales of smart health devices, which comprise 23 percent of the revenue for “millionaire” companies. For example, startup ZhongAn has promoted exercise trackers through its Bububao campaign. Customers receive free insurance if they use these devices and reach the goal of 15,000 daily steps. The company also promotes health insurance plans. All sources of revenue brought ZhongAn 16.88 billion USD in 2019 alone.
Health Insurance Reimbursement
Mobile health systems could find a new source of revenue if they perform diagnostic tests or provide therapeutic services. If the doctor prescribes an app (as is required in the United States), the company will be qualified for reimbursement under insurance plans.
There are examples of using this model already. The AliveCor Mobile ECG heart monitor, approved by the FDA, runs off iOS devices. Like regular clinical ECG monitoring, this device can be prescribed and qualifies for payment under private health insurance. So, if you receive the state medical commission’s approval and convince doctors to prescribe the app to patients, the income will be higher than the other models can give. Only AliveCor Inc. has reached 26.1 million USD in annual revenue per year; this is just one of many examples.
At CHI Software, we know how to create a health insurance app for such a business model and successfully implement solutions integrated with IoT-powered tools and smart devices for therapeutic services. See how it works in our baby care application for monitoring crucial health indicators.
Case study — a measuring device and a mobile app where parents can track characteristics remotely:
- Our team has designed an IoT wearable device: a cute baby ankle bracelet with sensors that continuously track oxygen saturation, pulse rate, and body temperature;
- We have developed an app connected with a bracelet to install on parents’ smartphones (Android or iOS);
- The bracelet’s sensors connect to the mobile app, transfer the results to a smartphone, and send alert signals via Wi-Fi.
The app and bracelet can be used in standard neonatal practice and newborns’ health insurance programs as a device to monitor the child’s vital indicators. After the solution’s certification, young parents will receive insurance compensation for the paid app services if a doctor prescribes them.
Technologies used: Ruby, Rails 4.2.6, PostgreSQL, Grape, Swagger, Ansible, RSpec, AES-256 encryption, Firebase Cloud Messaging, etc.
If you’re interested in software product development just like this – you know who to talk to. In the meantime, let’s cover how to build an insurance app.
Building an Insurance App: How to Succeed
You need expertise from a professional software development team to build health insurance software. An insurance app deals with vital services and extremely confidential data, so it must be high-performing and created without compromising quality. Any little thing can lead to threats to patients and material losses. Therefore, enlist the help of qualified business analysts, UI/UX designers, QAs, and frontend and backend developers who are experienced in insurance software development and follow a step-by-step plan:
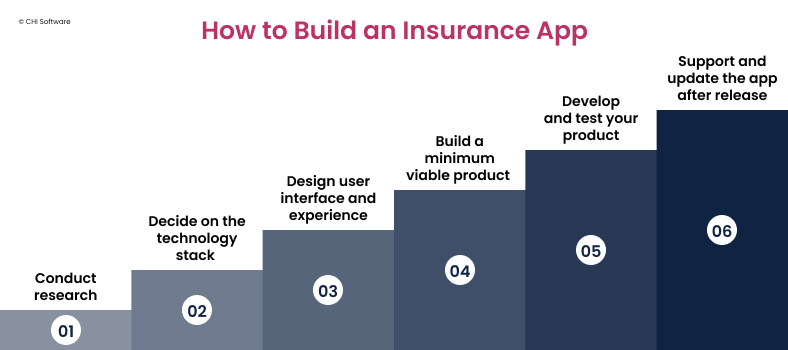
Step 1: Conduct Research
The primary stage of health insurance software development is business analysis, competitors and opportunities research, development costs estimation, the product’s market positioning, and listing the features. Here we should:
- Define business requirements and product architecture;
- Create the business plan and in-depth technical documentation;
- Elicit the best technical solutions.
At this stage, we find out how to create a product vision — a health insurance application’s roadmap. We build the design according to business goals and develop consistent information architecture. When formalizing the idea into the project scope, we should think about future implementations and ensure all solutions are scalable enough.
Step 2: Decide on the Technology Stack
The technology stack depends on the choice of the platform. This could be iOS, Android, or cross-platform. In the case of health insurance software, the iOS-only approach is best for the United States, while Android fits the rest of the world. Remember, iOS users spend three times as much as Android, but Apple customers’ quantity is less overall.
Swift is Apple’s official framework for health insurance software development (macOS, iOS, watchOS, and tvOS). If you’ve decided to serve iOS and Android devices, the React Native cross-platform framework is a smart choice. Its advantages are that it’s open source and has a significant memory allocation (but file sizes are more massive than Swift ones). Both platforms support third-party libraries and APIs.
mHealth App Development: The Complete Guide
Read more
According to the Research2Guidance report, 84 percent of health insurance apps took two years to launch, and the average time was 15 months. You can use ready-made tools to speed up insurance software development for up to three to six months. API integration is still challenging for developers, but we at CHI Software do it successfully.
Many handy tools are available: for example, the Twilio Programmable Video API works on iOS, Android, and all browsers without installing any plugins. The VSEE SDK integrates end-to-end encrypted video calling into your mobile app(and is HIPAA–compliant). VIDYO enables you to integrate real-time communications into your Mac, Windows, Linux, iOS, or Android app.
Step 3: Design User Interface and Experience (UI/UX)
This step of insurance software development is important for any software. The visual appeal defines customer satisfaction and engagement.
This is why UI/UX design should be based on devices’ parameters. The modern apps work on smartphones with a high aspect ratio (18:9) and bezel-less display. Apple uses 1x, 2x, and 3x sizes, and in the case of Android, designers must ensure compatibility with six sizes — from 120 dpi LDPI to XXXHDPI.
Another challenge of health insurance software development is the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and augmented reality (AR) technologies. We at CHI Software use them actively, and our designers know how to work with them. Technologies make health insurance application environments interactive, and the design needs to take into account new patterns and virtual objects that may be integrated.
The insurance app should be convenient for patients with any physical abilities. Therefore:
- Take the time to review the WCAG 2.0 Guidelines for W3C recommendations and online content accessibility best practices;
- Simplify the adaptation process as much as possible by limiting the number of screens to a maximum of three;
- Consider one-handed navigation and thumb-friendly layout; and
- Use correct spacing: the tap area’s preferred size is 7–10 mm. The screen top is hard to reach, and in the case of larger sizes, it requires a change of grip.
Step 4: Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)

The MVP is a version of an app that contains the lowest number of features that satisfy early customers and allow for the gathering of user feedback. Its creation aims at hypothesis validation, risk mitigation, fast product release, and better feature prioritization.
The MVP version of the insurance app should provide users with simple must-have functionality:
- Admin panel and user profile;
- Doctor’s appointment booking;
- Secure video calls and conferencing;
- Chats/chatbots;
- Recording for reception;
- Claims processing;
- Database.
A prototype and MVP must be tested on a real audience to learn about users’ interactions with the product. After feedback collection and characteristics/functions refinement, we can proceed to the health insurance software development stage.
Step 5. Develop and Test Your Product
After you ensure that your MVP succeeds, you can proceed with the insurance app development. It is worth adding features here that will further improve the service quality and bring more comfort to patients and doctors:
- AI-powered diagnostics;
- EMR/HER and HIS (health information system) integration;
- IoT-based tools and peripherals;
- VR/AR capabilities;
- E-prescribing, dosing calculators, and drug-interaction checking;
- Shared knowledge base and medical newsfeed;
- Patient progress tracking, predictive analytics, etc.
After the app development process, you have to fix bugs. With the help of testing engineers, you must ensure that the product meets the most stringent quality standards. For mobile apps, we at CHI Software apply QA service after insurance software development, covering the entire lifecycle, checking the software on multiple platforms and devices, and providing various types of testing:
- Functional and interoperability;
- Security and access control;
- Non-functional;
- Usability;
- Change-related;
- Structural.
After developing and testing your health insurance application, you are ready to deliver the product and move it to app stores.
Step 6: Support and Update Your App After Release
It is not enough to know the steps of health insurance software development of your health insurance app and sell it to customers. Remember that iOS and Android get updates every year. It is important that your application is up–to–date and works correctly on the latest platforms. Qualified post-release support and maintenance ensure scalability, quick implementation of new features, the best possible interaction of the system with the user, and consistently bring new customers and stable revenue.
Every development process has its quirks and challenges, so it’s logical that insurance apps have them too. Let’s talk about them.
Challenges of Health Insurance Apps
Health insurance software solutions aren’t necessarily simple. Consider that healthcare is complicated to navigate, clinics are slow in decision–making, and there are many challenges to face while developing a health insurance app.

Sharing Medical Data With Patients, Health Insurance Systems, and Partners
In 2019, the CCM conducted a survey, during which it discovered that almost 30 percent of healthcare facilities needed more interaction, even for their departments. The data exchange with third-party systems has been successful in even fewer cases. Pieces of information are spread across multiple organizations, and it is difficult for providers to streamline document management due to the amount of data gathered for years.
Interoperability problems of health insurance app development can be solved by open and custom APIs that:
- Help to transfer claims data between systems quickly;
- Improve communications and customer service;
- Allow the creation of apps that can schedule doctor’s appointments and manage chronic diseases like diabetes.
As we at CHI Software know from practical experience, API integration tools can save time and money when developing your health insurance application. They allow linking data points from multiple sources to create complete sets to improve analytics and treatment results. Making a health insurance mobile application with third-party software integration becomes transparent, and all patient history is consolidated in one place.
AI Matchmaking: Choosing the Right AI Expertise for Your Business Goals
Read more
Data Security, Privacy, and Protection
Robust security measures are the top challenge for everyone interested in insurance software development and mHealth. First and foremost, the application should have a flawless privacy policy, and the owner has to provide access to it before the health insurance software is downloaded.
It is recommended to use APIs when you create a mobile health insurance app. They ensure multi-level data safety and provide threat prevention tools. At CHI Software, we also successfully implement cloud solutions like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to achieve the level of data protection that meets the most security-sensitive organizations’ requirements.
The app’s safety can also be ensured with:
- Tiered application and database access — a strict password policy, authentication by Touch-ID or Face Recognition module, etc.;
- An encrypted communication layer and secure SSL connection protocols that protect data being exchanged between customers and the server;
- Role-based authentication and permissions management; and
- Suspicious activity and brute force app login detection and prevention.
EHR Interoperability
Despite improvements in EHR technology, it still contributes to data silos, and interoperability remains an issue. When developing health insurance software, it is challenging to recognize a specific patient in the EHR system, as there are no common standards or single identifiers for customers. Medical professionals have to invest a lot of time comparing all e-records and finding information about a person in them.
APIs can also address the reasons behind EHRs’ mess. They provide an instant connection with e-records and other existing data references. To ensure secure integration with a third-party EHR, we can establish a VPN tunnel that connects a hardware-driven VPN gateway on the client side with a virtual VPN gateway on the app’s side.
Health App Regulations
When creating a health insurance app, you must always ensure compliance with legislation regarding commercial healthcare services and medical data processing. Here are the main ones:
- HIPAA: This American act and HITECH (a list of additions to HIPAA) dictate the standards for collecting and processing sensitive medical data for every health insurance company.
- GDPR, Data Protection Directive, and e-Privacy Directive: The EU regulates data processing according to privacy rules and human rights laws and only permits confidential data processing based on transparency, proportionality of use, and legality.
- PIPEDA: You need to follow this federal law if you create a health insurance app for Canada and proceed with using personal health information for commercial purposes.
- PCI-DSS Compliance: If your health insurance software has a payment gateway and collects and processes cardholder data, you must ensure PCI-DSS compliance. This standard applies to all who accept card payments, even if only mobile application integrations exist.
Conclusion
Such a huge market as the healthcare sector needs to be more modern and convenient for everyone, and apps have already become an effective way to improve the customer experience.
Health insurance software has enormous value for users. The apps simplify the health monitoring process, save time, and optimize everything that goes in between the patient’s initial issue and recovery. Building a custom healthcare insurance app is a win-win strategy, helping your clients get quality health insurance while allowing your insurance company to be competitive and make money successfully.
Currently, not all insurance companies have progressive and convenient health insurance software, but they learn quickly. Therefore, there won’t be a better moment for developing a health insurance application than now. Request healthcare AI consulting from us, and we will help you create the best solution for your business!
About the author
Anton Panteleimenko
iOS Developer
Anton is a skilled iOS developer with a knack for building user-friendly and modern mobile apps. Always eager to explore new technologies, he stays up-to-date with the latest trends in iOS development and remains at the forefront of mobile engineering.










